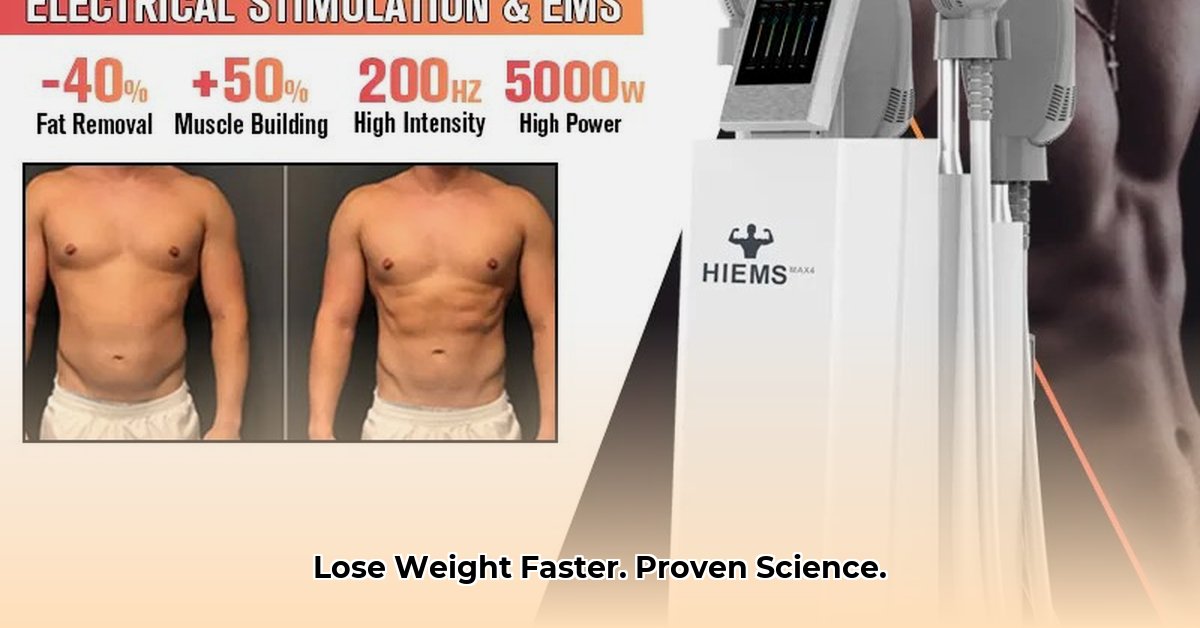
So, you're considering EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) for weight loss? The market buzz is significant, but does the science support the hype? This article analyzes the evidence-based research, providing a balanced perspective on EMS's role in achieving weight loss goals.
Understanding Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
EMS uses mild electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions. Imagine a targeted, intense workout, without the typical exertion. These contractions build muscle strength, and some believe this translates to effective weight loss. However, the reality is more nuanced.
Does EMS Actually Help You Shed Pounds?
The effectiveness of EMS for weight loss is complex and not definitively proven. Some studies suggest improvements in muscle strength and body composition (a leaner physique). However, other research shows less dramatic results, particularly for individuals already engaging in regular exercise. The impact of EMS on weight loss appears highly dependent on several factors, each significantly influencing the overall outcomes.
Key Factors Affecting EMS Weight Loss Success
Consider EMS weight loss a multifaceted puzzle, with several crucial pieces:
- Training Intensity and Duration: Higher intensity sessions may yield better results, but overtraining risks injury and soreness. Consistency is paramount; gradual progress is more sustainable than rapid, unsustainable efforts.
- Pre-existing Fitness Level: Beginners may experience more noticeable improvements compared to seasoned athletes, for whom the gains might be less significant.
- EMS Machine Quality: Not all EMS machines are created equal. Choosing a reputable brand with high-quality equipment is essential for optimal and safe results.
EMS vs. Traditional Exercise: A Balanced Comparison
Is EMS superior to traditional workouts? The answer is not straightforward. EMS offers convenience, but it's most effective as part of a comprehensive fitness program, not as a standalone solution. Traditional exercise provides broader benefits, improving cardiovascular health, stamina, and flexibility—aspects EMS may not fully address.
Weighing the Pros and Cons of EMS for Weight Loss
A balanced perspective requires acknowledging both the advantages and limitations of EMS for weight loss:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Time-efficient workouts | Potential for muscle soreness and discomfort |
| Improved muscle strength and tone | Inconsistent results across studies; research is still ongoing |
| Can contribute to a successful weight loss strategy | Relatively high cost of equipment or professional treatments |
| Convenient option for busy individuals | Not a miracle cure; significant weight loss requires a holistic approach |
A Practical Guide to Safe and Effective EMS Use
To maximize the benefits of EMS while minimizing risks:
- Consult Your Physician: Before starting any new fitness regimen, including EMS, seek your doctor's advice to ensure its suitability for your health status.
- Choose a Reputable Provider: Select a facility with well-maintained equipment and certified trainers to guarantee safety and efficacy.
- Gradual Intensity Increase: Begin with lower intensity sessions and gradually increase intensity to avoid overexertion and injuries.
- Integrate with Other Activities: Combine EMS with other forms of exercise, such as cardio and strength training, and maintain a balanced diet for optimal results.
- Listen to Your Body: Rest when needed and avoid pushing yourself beyond your limits to prevent injuries.
The Future of EMS and Weight Loss Research
Research on EMS and weight loss continues to evolve. Future studies may refine training protocols, potentially leading to more personalized and effective EMS programs. While promising, EMS is not a standalone solution. A holistic approach encompassing healthy diet, varied exercises, and lifestyle changes remains crucial for lasting weight management success.
EMS Weight Loss: How Effective Is EMS Training for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain?
Key Takeaways:
- EMS utilizes electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions, potentially aiding in building strength and contributing to weight loss.
- The effectiveness of EMS is highly variable and depends on factors such as training programs, individual physiological responses, and integration with other exercise forms.
- Studies show varying results, with some indicating improvements in muscle mass and fat reduction, while others find minimal benefit compared to standard exercise regimes.
- Further research is needed to optimize EMS training protocols and identify individuals who would benefit most.
- Combining EMS with other exercise modalities may enhance its impact.
- Be aware of potential side effects including skin irritation and muscle soreness.
Understanding Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS)
EMS uses electrical impulses to trigger muscle contractions, providing a unique workout experience. However, the question remains: How effective is EMS training for weight loss and muscle gain? The answer requires a comprehensive understanding of the evidence.
EMS and Muscle Growth: A Scientific Perspective
Studies demonstrate EMS's ability to build muscle strength, especially in lower body and core muscles, often with more noticeable results in shorter training periods. However, the extent to which it surpasses traditional weight training remains debated. Some research indicates no significant difference, specifically for experienced athletes. Methodological inconsistencies across studies hamper conclusive evaluations.
EMS and Weight Loss: Dissecting the Evidence
EMS can contribute to weight loss; however, it is not a standalone solution. Muscle building increases resting metabolic rate, potentially leading to a slight boost in calorie expenditure. However, the extent of weight loss largely hinges on factors such as diet and overall activity levels. It's not a replacement for a healthy lifestyle.
Factors Modulating EMS Effectiveness
Several factors influence EMS efficacy:
- EMS Device Type: Whole-body versus localized EMS devices exhibit different effects.
- Electrode Placement: Precise electrode placement is crucial for effective muscle stimulation.
- Intensity Levels: A gradual increase in intensity is crucial to preventing injuries and maximizing gains.
- Exercise Integration: Combining EMS with other forms of exercise often optimizes results.
- Individual Physiological Factors: Age, gender, fitness levels, genetics, and existing health conditions all play a role.
Potential Risks and Side Effects Associated with EMS
While generally safe, EMS carries potential risks:
- Skin Irritation: Proper electrode placement and gel application minimize this risk.
- Muscle Soreness: Expect some muscle soreness, especially initially. Start slowly and prioritize recovery time.
- Electrical Burns (Rare): Use certified devices and follow instructions to minimize this risk.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias (Rare): Individuals with pre-existing heart conditions must consult their physician before using EMS.
Optimizing Your EMS Workout
To maximize results from EMS:
- Certified Trainer: Work with a certified trainer to ensure proper technique and safety.
- Combined Exercise: Integrate EMS with other forms of exercise; it serves as a supplement, not a complete workout.
- Attentive Listening to Your Body: Stop if you experience any discomfort and adjust accordingly.
- Patience: Results take time, like any other fitness program.
Conclusion: The Bottom Line on EMS for Weight Loss
The effectiveness of EMS training for both weight loss and muscle gain is not straightforward. While showing potential benefits, its efficacy varies greatly. For optimal results, combine EMS with a holistic approach encompassing a balanced diet and regular exercise.